With over 300 days of sunshine a year, Cyprus is the perfect location to harness the power of photovoltaic technology. With our solar panels and inverters converting sunlight directly into clean, renewable energy, you can significantly lower your electricity bills. It’s a smart investment for your home or business that not only boosts your property value and reduces electricity costs but also helps you to limit your carbon footprint in a country where solar power is a natural resource.

What is a Photovoltaic System?
A photovoltaic (PV) system captures sunlight and converts it into electricity. The system includes solar panels absorbing sunlight and an inverter to convert the electricity to a usable form, providing an eco-friendly and renewable energy source for homes and businesses. By installing a PV system, you can significantly reduce your electricity bills and become less reliant on conventional energy sources.
One of the key benefits of photovoltaic systems is financial savings. With the abundant sunshine in Cyprus, a PV system can quickly pay for itself, typically within three to four years, thanks to the reduced energy costs. After this period, the energy you generate is essentially free, making it a smart long-term investment. Additionally, PV systems can increase the value of your property.
By choosing solar power, you not only save money but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
What is Net Metering?
Net Metering is a billing mechanism that enables you to generate your own electricity using solar systems and store any energy surplus produced in the electric grid. This is the way it works:
1. Electricity Generation: Your solar panels and inverter generate electricity, which is first used to power your home or business.
2. Electricity Surplus: If your solar system produces more electricity than you need, the energy excess is sent to the grid. This is mostly the case during sunny days when production is high.
3. Credit System: The excess electricity you send to the grid is converted into credits on your electricity bill. This means you are effectively “storing” energy in the grid.
4. Usage of Credits: When your solar system is not generating enough electricity, such as at night or on cloudy days, you can use the collected credits to use power from the grid without additional costs, besides minor grid charges.
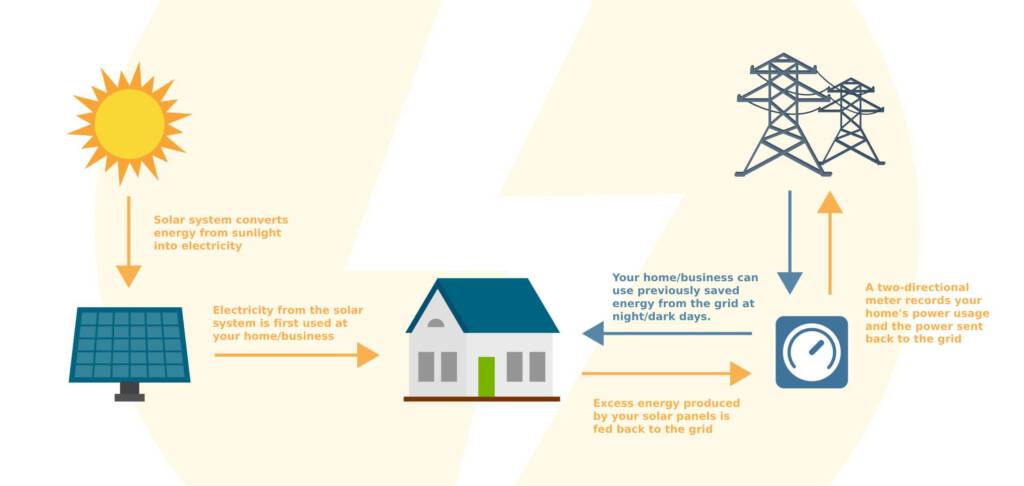
Regulations in Cyprus:
• For residential properties, Net Metering is allowed for PV systems up to 10 kW
• For commercial properties, Net Metering is allowed for PV systems up to 30 kW.
Net Metering allows you reduce your electricity bills and makes your investment in solar energy more cost-effective by making it possible to use the grid as a backup storage system.

What is Net Billing?
Net Billing enables you to sell electricity surplus from your solar panels back to the grid and receive compensation. This is the way it works:
1. Electricity Generation: Your solar system generates electricity for your home or business.
2. Electricity Surplus: Excess electricity is sent to the grid.
3. Compensation: You receive payment for the electricity surplus which is typically lower than what you pay for grid electricity. This remuneration offsets your electricity bills.
4. Electricity Usage: When solar system energy production is low (e.g., at night), you use electricity from the grid and pay the regular rate.
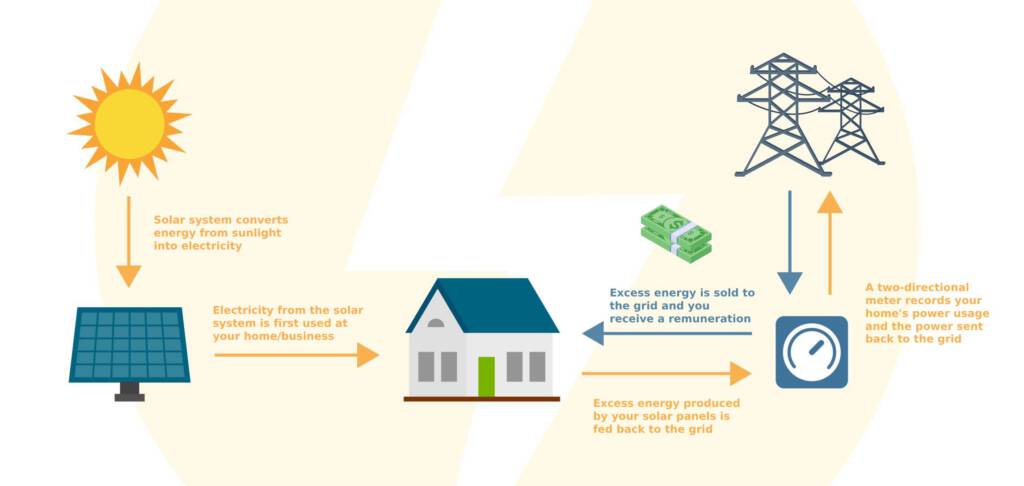
Regulations in Cyprus:
• Suitable for larger systems, especially for commercial and industrial users to generate income from electricity surplus
• Applies to systems starting from 10 kW.
Difference between Net Metering and Net Billing:
| Net Metering | Net Billing | |
| System Size | Up to 10 kW (for residential properties) | Over 10 kW (recommended for commercial properties) |
| Electricity Usage | Direct offset of electricity consumption | Selling excess electricity to the grid |
| Compensation | Credit for energy surplus against future bills | Earning for excess electricity (7-9 cents per kWh) |
| Best for | Residential properties with smaller systems | Larger systems (residential, commercial, industrial) |
| Financial Benefit | Greater focus on self-consumption savings | Focus on selling electricity to the grid |



